Executive Summary
- Increasing need for reducing energy consumption is driving the growth for smart lighting solutions. Smart lighting has the potential to reduce energy costs by 90 percent as per Gartner.
- Smart lighting is an integrated system that involves segments such as light sources, luminaries, sensors & control units, connectivity, and analytics. Implementation involves combining these elements that offer lighting solutions that can be monitored, controlled and automated using a centralized system.
- Well known players in this industry are Phillips (the Netherlands), Osram (Germany), Lutron (USA), Legrand (France), Daintree Networks (the U.S.), Bridgelux (the U.S.), Echelon Corporation (the U.S.).
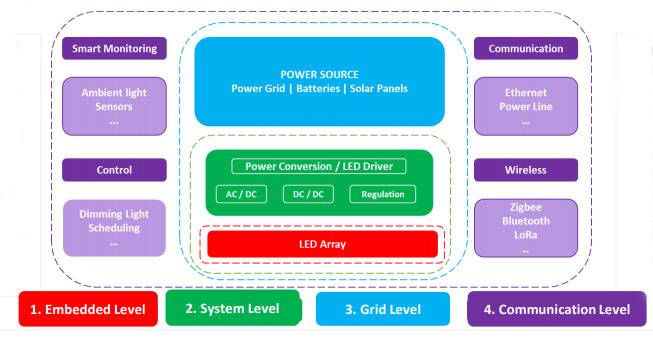
- Fabricating a smart lighting system involves multiple phases. For example, the first level is the embedded level which consists of a lighting engine. It is an LED chip mounted on a circuit board that has electrical and mechanical fixings. The next level is the system level that involves connecting the luminaires and lighting systems. The third level performs the energy management function. The fourth level involves adding connectivity to the smart lighting system to provide automation and intelligent features.
- There are several products available within the segments of smart lighting
- The GE In-Wall Lighting Control switches are designed to connect to a smart home hub and activate with your mobile device.
- Philips Hue personal wireless lighting system.
- Osram’s ENCELIUM® EXTEND, Networked Light Management System to manage interior and exterior commercial lighting spaces.
- There are many interesting trends evolving for smart lighting applications. Following are a few examples –
- Government organizations in different countries have significant programs for street lighting using solid state technology, and HID (High Intensity Discharge) or LED (Light-emitting diode) lamps to create connected street lighting. They provide many benefits such as reduced consumption of energy, real-time monitoring, safety, security, monitoring air quality and traffic & pedestrian monitoring, etc.
- Smart lighting is being implemented to change ambience lighting real-time, provide responsive control to occupant activities in offices, retail stores, hospitals, educations institutions, and residential buildings.
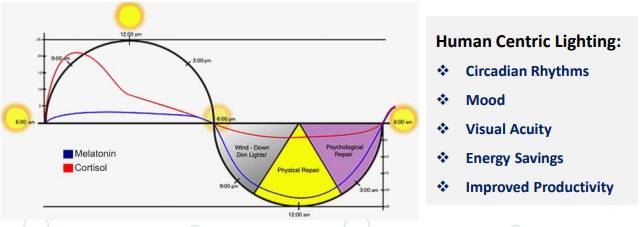
- In addition, smart lighting is being considered for innovative applications such as vertical farming, human-centric lighting, etc.
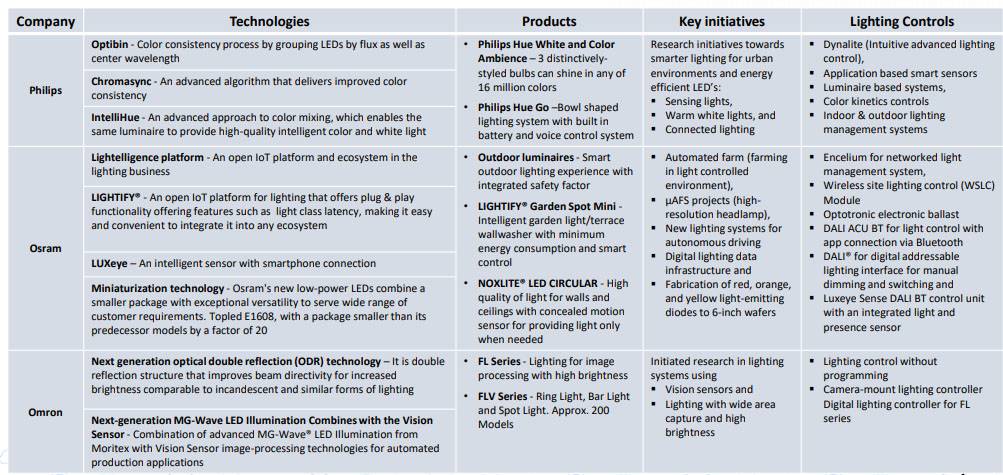
- There are several technologies that are being developed within various segments of smart lighting
- Protocols for smart communication protocols such as Internet Protocol for Smart Objects (IPSO, 6LoWPAN, one of IoT communication protocols, Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP) and others.
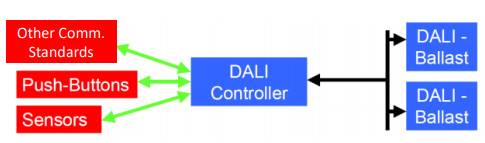
- Lighting protocols such as – Digital Addressable Lighting Interface (DALI®), Digital Load-Side Transmission Lighting Control (DLT), Digital Multiplex, Digital Serial Interface, etc.
- To increase illumination, technologies such as laser diodes using sulphur configuration and optical double reflection are being developed.
Introduction
Smart Lighting is an illumination management system that consists of a variety of sensors, controllers, video processing units and information & communication technologies. It is widely used for indoor, outdoor, and industrial applications.
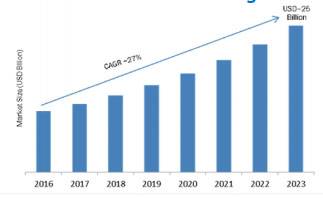
Growing need for energy efficient and cost-effective solutions is driving the growth of the smart lighting market. Globally, the smart lighting market is expected to grow at approx. USD 25 Billion by 2023, at 27% of CAGR between 2016 and 2023 Europe, followed by North America is projected to hold the highest market share of the global smart lighting market by 2023, while Asia-Pacific is projected to grow at the fastest rate. The major growth in smart lighting market in Europe is attributed to technical advancements and increasing investments in infrastructure projects