INTRODUCTION
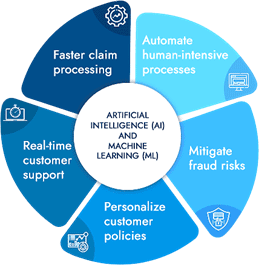
The evolution of technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Big Data, Blockchain, Cloud Computing and others have positively impacted the insurance industry. Digitization has not only helped automate numerous operations, but has also enhanced customer experience. Appreciating the fact that digitization is the key to developing the industry has resulted in several startups entering the space and numerous investments being made. This paper highlights the technologies that have impacted the insurance industry. It also touches upon the avenues that have opened up for the industry in terms of new products and also innovative ways of doing business.

 StrongArm Technologies Inc. (‘StrongArm’), a safety science company, has developed a data-driven wearable technology (Fuse Flex8) that helps in preventing workplace injuries by monitoring the employees and providing real-time alerts. StrongArm’s patent –
StrongArm Technologies Inc. (‘StrongArm’), a safety science company, has developed a data-driven wearable technology (Fuse Flex8) that helps in preventing workplace injuries by monitoring the employees and providing real-time alerts. StrongArm’s patent –