INTRODUCTION
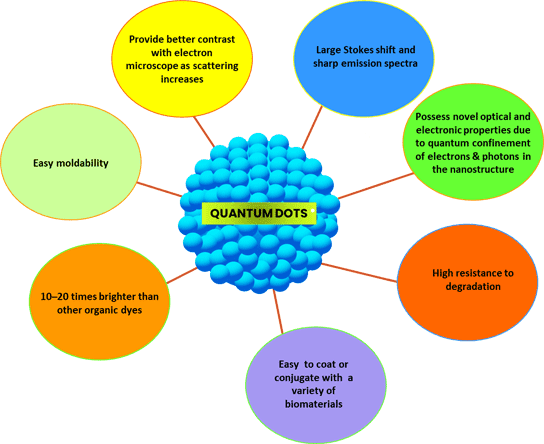
Development of nano-theranostic platforms, particularly those based on quantum dots (QDs) for simultaneous sensing, imaging and therapy, have evinced interest in researchers in recent years. The major advantage with the use of QDs is the possibility of achieving high precision in controlling the conductive properties of the material through the control of their crystal size.
The physicochemical properties of QDs (Figure 1) have enabled their application in various domains such as single-electron transistors, solar cells, LEDs, displays, lasers, photodetector devices, photocatalysts, photovoltaic devices, quantum computing, forensic, microscopy, and medicine.[1]