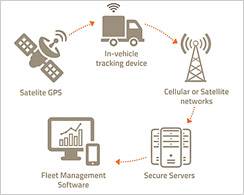
INTRODUCTION
With the exponential expansion of the e-commerce space, proper logistics management has become vital, especially to keep up with the fast pace of demand and supply. More recently, warehouses or fulfilment centers have been handling an unbelievable increase in the volume of goods. Transportation of goods has also become challenging following the need to transport and deliver goods in a timely manner without compromising on quality and safety. Some areas that cause concern to the logistics companies include:
- Increased transportation costs
- Manual errors of operators
- Loss or theft of goods
- Cyber security
- Regulatory requirements
- Expectations of customers
This paper aims at understanding how certain tools, devices and softwares leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI), Blockchain, Big Data, Machine Learning (ML) and the Internet of Things (IoT) address the concerns of the logistics operators. It also presents examples of investments made and restructuring exercises that have occurred in the logistics space.
WAREHOUSING
Warehousing technologies aim at reducing costs, improving efficiency, automating repetitive tasks and streamlining operations. Optimization of warehouse operations and enhanced labor productivity that allows for seamless, fast and error-free functioning have been made possible by the application of technologies. Beside warehouse optimization, there are regulatory aspects to be adhered to in terms of maintenance of data regarding goods and other documents, in addition to quality control. A few warehousing automations that have aided the logistics sector in terms of speeding up processes and achieving higher accuracy and efficiency are discussed below.
DIMENSIONING SYSTEMS
Dimensioning systems have been leveraged to calibrate dimensional information (measurements) of the boxes/pallets and include the same in the warehousing receipt. Dimensioning systems allow the space in the warehouse to be utilized in an optimal manner. Integration of dimensioning systems with the Warehouse Management System (WMS) reduces errors in the entry of data and prohibits duplicity, since the data is simultaneously logged into multiple devices automatically. The dimensioning module includes the communication module, photoelectric sensors, mounting frames and Human Machine Interface (HMI)/ operator panels. The weight measuring modules consist of a weighing processor, a processor to control the conveyor and transmit the data to WMS, a strain gauge transducer for converting weight data to electric signals, rollers and profiles, and photoelectric sensors.