Automotive manufacturing witnesses the highest deployment of robotic automation. Welding, assembly, machine tending, material removal, part transfer etc. are the assembly operations best suited to robotic automation. However, when it comes to tasks that need judgement and decision making, there is still scope for improvement in the performance of robots. Wire harness is the nervous system of automobiles, consisting of wire and connector assemblies of multiple sizes and shapes. The harness carries various control and power signals between the main control unit, battery and various parts of the automobile. Assembling such cables with connectors requires high levels of skill and is most time -consuming. It involves pairing the cables with appropriate connectors and fixing the complex wiring structure inside the automobile. The task of installing wire harnesses in car bodies has traditionally been difficult for robots. Therefore, multiple approaches such as simplifying the harness architecture and improving the robot’s capabilities are being adopted to solve the complex problems associated with wire harness.
Simplification of the harness architecture
A recent patent publication (US20190217794) on modular wiring harness attracted global attention. The patent application from Tesla claims ease of assembling the wiring harness during vehicle manufacture. The patent also discloses reduction in the total length of wires.
The patent application identifies problems in wire harness and provides solutions as listed below:
| Critical issues with existing wire harness | Solutions provided by Tesla |
|---|---|
| Multiple wiring systems are needed to connect different electrical components to different harnesses. | Packaged subsystems are defined for each assembly so that the number of connections to the main hub is minimized. |
| Connectors for current harness systems are not so rigid. | Tesla’s application reveals more rigid wiring architecture that is easy for robots to manipulate. |
| Assembling wire harness is currently done by skilled workers as it is considered to be difficult for automation by robots. | Sub-assemblies reduce wire lengths, enabling assembly by robots. |
Tesla’s innovative wiring architecture presented in the patent application is reproduced below.

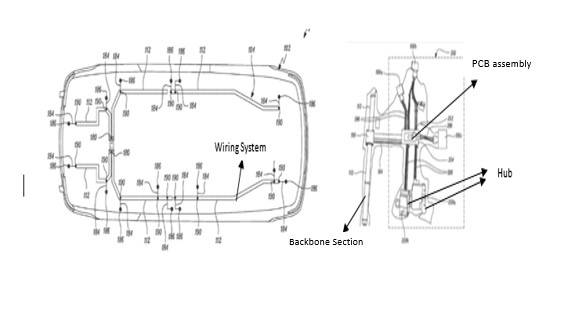
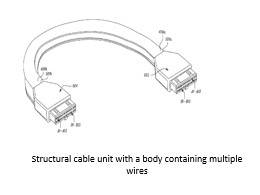 “structural cable” so that robotic arms can handle them with ease. Patent application US20180294075 from Tesla explains a structural cable with multiple collinear wires or conductors formed together to maintain rigidity and integrity. These cables can be handled by robots in automated assemblies.
“structural cable” so that robotic arms can handle them with ease. Patent application US20180294075 from Tesla explains a structural cable with multiple collinear wires or conductors formed together to maintain rigidity and integrity. These cables can be handled by robots in automated assemblies. printed circuit technology, has employed its technology for temperature and voltage monitoring circuits in EV battery packs. Use of Flexible Printed Circuit Boards can contribute to approximately 75% weight reduction as compared to conventional wiring harnesses.
printed circuit technology, has employed its technology for temperature and voltage monitoring circuits in EV battery packs. Use of Flexible Printed Circuit Boards can contribute to approximately 75% weight reduction as compared to conventional wiring harnesses. facilitates manufacturing of flexible printed circuits of any length. Recently, the company manufactured the world’s first and longest FPC of 26 meters which supports control and transmission of power and communication signals without the need for an additional wire harness. Currently, this technology is being employed in space vehicles due to its lightweight benefits, and may be adopted in automotive to attain equivalent benefits.
facilitates manufacturing of flexible printed circuits of any length. Recently, the company manufactured the world’s first and longest FPC of 26 meters which supports control and transmission of power and communication signals without the need for an additional wire harness. Currently, this technology is being employed in space vehicles due to its lightweight benefits, and may be adopted in automotive to attain equivalent benefits.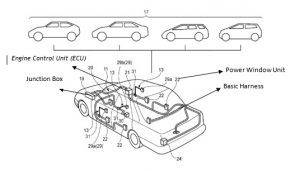 electronic control unit (ECU) to the electronic devices in the extension system. The company was recently awarded a patent (
electronic control unit (ECU) to the electronic devices in the extension system. The company was recently awarded a patent (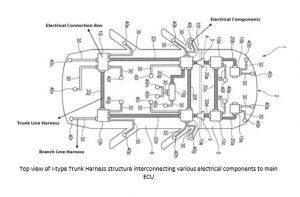 structure of the circuit body can be simplified while connecting a power source and an electrical component. The number of electric wires constituting the trunk line harness has been reduced by inserting the trunk line harness through a hollow portion of a tubular exterior member (for example, like a grommet for stopping water). This is much easier as compared to a typical wiring in a circuit body.
structure of the circuit body can be simplified while connecting a power source and an electrical component. The number of electric wires constituting the trunk line harness has been reduced by inserting the trunk line harness through a hollow portion of a tubular exterior member (for example, like a grommet for stopping water). This is much easier as compared to a typical wiring in a circuit body.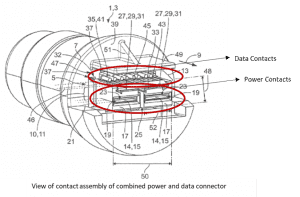 power and data connector capable of transmitting both data and power. The connector has a first section that carries data signals with data contacts that are capable of carrying currents up to 1 Amp. The second section may be adapted as a power section separated from the data section, with additional power contacts for transmitting power that exceeds PoE limit of data contacts.
power and data connector capable of transmitting both data and power. The connector has a first section that carries data signals with data contacts that are capable of carrying currents up to 1 Amp. The second section may be adapted as a power section separated from the data section, with additional power contacts for transmitting power that exceeds PoE limit of data contacts.
 shear stress and force that occur while performing tasks. The bio-skin sensor can actually mimic human finger functionality by experiencing tension and compression as it moves or slides along the objects. The flexible electronic skin, which is wrapped around the robot finger, is the first of its kind to measure shear tension similar to that of a human hand. This prosthetic hand is capable of sensing whether it is sliding through an object or holding it with the help of e-Skin made of rubber containing electrically conductive liquid metal. As the tension forces change along the surface of the liquid metal, the electrical potentials change, which indicates certain action performed by the finger. This can assist in sensing very minute forces so that tasks like dismantling an explosive or holding a surgical instrument while handling robotic surgeries might be easier and time saving.
shear stress and force that occur while performing tasks. The bio-skin sensor can actually mimic human finger functionality by experiencing tension and compression as it moves or slides along the objects. The flexible electronic skin, which is wrapped around the robot finger, is the first of its kind to measure shear tension similar to that of a human hand. This prosthetic hand is capable of sensing whether it is sliding through an object or holding it with the help of e-Skin made of rubber containing electrically conductive liquid metal. As the tension forces change along the surface of the liquid metal, the electrical potentials change, which indicates certain action performed by the finger. This can assist in sensing very minute forces so that tasks like dismantling an explosive or holding a surgical instrument while handling robotic surgeries might be easier and time saving.