With food waste being the most serious problem facing the food industry today, upcycling is considered a sustainable way of managing the same. Food waste can be recycled into food ingredients and cosmetics. Among the various processing techniques, fermentation, pulsed electric field assisted extraction, pressurized liquid extraction, supercritical fluid extraction, membrane-based separation and spray drying technology are well known. Arla Foods, in collaboration with Enorm, an insect farm, upcycled the de lactose permeate (DLP) having high nutritional value, as a feed for insect larvae. Companies such as Kaffe Bueno, Solabia, Symrise and Swisse Wellness utilize food waste and food by-products in cosmetics and perfume ingredients. Lack of consumer awareness and acceptance hinders commercialization of upcycled products and therefore, must be overcome to achieve a zero-waste sustainable economy.
Introduction
18th March was established as Global recycling day by the Global Recycling Foundation, a non-profit organization, with the aim of promoting awareness of waste recycling and sustainable development. The day has been recognized by the United Nations and is being celebrated across the world.
Among the various waste materials polluting our environment, food waste plays a significant role due to the generation of greenhouse gases such as methane. According to statistics, about 1.3 billion tons of food suitable for human consumptions are wasted every year. UNEP Food Waste Index Report (2021) has shown that around 931 million tons of food waste have been generated in 2019 out of which 61% were from households, 26% from food service and 13% from retail. Figure 1 shows the estimated household food waste (in million tons per year) in different continents as per UNEP Food Waste Index Report 2021 [1]
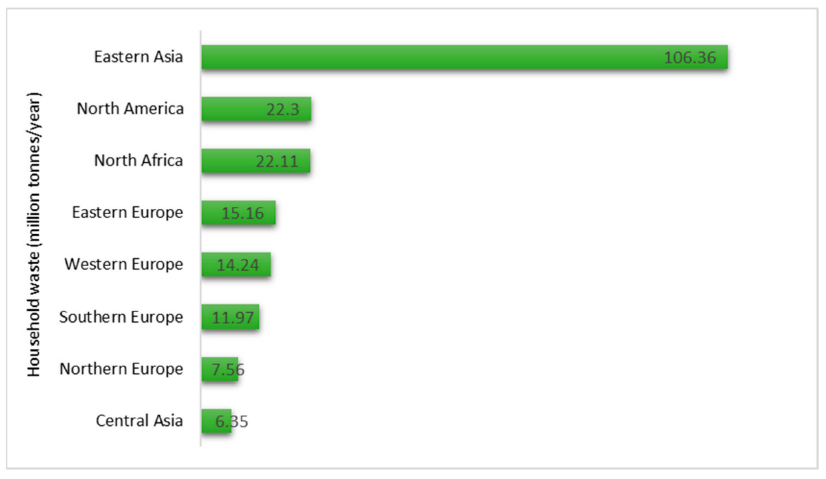 Figure 1
Figure 1
Due to their high carbon content and nutrients, food wastes including rotten/ damaged food or food parts, residues, by-products and left overs of food processing industries are considered a valuable feedstock for their conversions into value added products through processes such as composting, anaerobic digestion, bioconversion, and upcycling. The simple and cost-effective conventional ways of managing food wastes through landfilling and incineration suffer from various environmental issues and global warming [2]. Upcycling adds value to food wastes and has been considered as the most sustainable way of food waste management as shown in Figure 2.
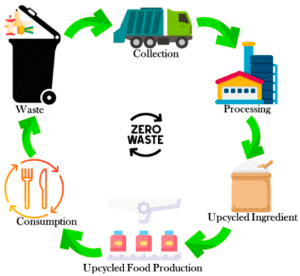
Figure 2
What are the recent processing techniques developed for upcycling of food waste?
- Fermentation process: Upcycling of food or food ingredients using fermentation processes have been attempted in the recent years. Fermentative preparation of lactic acid to be used as food preservative, from various food waste materials such as date palm waste, pasta waste and household food wastes using lactic acid bacteria (LAB) have been studied [3, 4, 5].
- Pulsed electric field (PEF): PEF assisted extraction of valuable compounds such as aroma and bioactive compounds (vanillin, theobromine, caffeine, linalool, limonene) from food waste such as vanilla pods, cocoa bean shells, orange peels etc. by using minimal amount of solvents and energy has been investigated very recently [6, 7].
- Pressurized liquid extraction (PLE): Bioactive compounds extracted from agro-industrial and marine life waste have been incorporated in nutraceutical products using combined techniques such as pressurized liquid extraction (PLE) and supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) [8].
- Membrane Technology: Huge amount of acid whey is being generated every year from dairy industry – approx. 1.5 million tons in USA, 4 million tons in Germany. Acid whey is considered as potential source of protein [9]. Studies have shown efficient isolation and value addition of whey protein fractions originating from dairy wastes and by-products of cheese and yogurt manufacturing plants by using membrane technology for food and pharmaceutical applications [10].
- Spray drying technology: US2022232846A assigned to University of Missouri, USA, relates to the preparation of acid whey-based food product in powder form utilizing spray drying technology using a mixture of acid whey and flour [11].
What are the innovations from some of the players?
- In dairy farms, during the production of lactose, huge amount of de-lactosed permeate (DLP) is wasted. Arla Foods, in collaboration with Enorm, an insect farm, upcycled the DLP having high nutritional value as a feed for larvae of the black soldier fly; ENORM has commissioned an upcycling plant in Flemming, Denmark, for this purpose [12].
- San Francisco–based startup Planetarians upcycles protein-rich food waste such as spent oil cakes and beans/yeast to produce various protein enriched food products, as well as vegan meat having same taste, flavor and texture as that of animal meat. The Planetarians’ savory strips are reported to have carbon footprint 50x better than animal meat and 10x better than vegetarian meat. Planetarians erected its first commercial facility in association with Ab InBev, a brewer company [13].
How is recycled food being used in cosmetics?
Upcycling of food waste and food by-products resulting in cosmetics and perfume ingredients meet customer demands in a sustainable manner.
- Denmark based company Kaffe Bueno considered spent coffee grounds rich in antioxidants, fatty acids, diterpene esters, proteins, sugars and other compounds, as a source for upcycling and used coffee-derived ingredients in various personal care products such as oils, shampoos, conditioners, creams, lotions, sunscreens etc. [14].
- Polyphenol rich coffee cherries or cascara, also waste products from the coffee industry, have been used by a French company Solabia as beauty booster. Solabia also used lemon peels and pearlescent oyster for upcycling in cosmetics [15].
- Symrise, a pioneer in flavors and fragrances market, bagged the 2023 BSB Environment Award for its unique, SymFrequencyTM a hyper-frequency extraction technology that involves safe solvents such as water or water/ethanol system. The sustainable extraction of upcycled oils such as apple oil, elderberry oil, and papaya oil from various by-products contains antioxidants, and possess moisturization as well as hair care properties [16].
- An initiative to upcycle huge amount of grape marc (pomace) from wine industry has been taken up by Swisse Wellness in association with Fight Food Waste Cooperative Research Centre (CRC) and Swinburne University of Technology to convert it into nutraceutical ingredients having antioxidant and collagen formation properties [17]
What are the products from some of the players?
Studies have shown that upcycling of food by-products and wastes are not confined to research stage. Entrepreneurs are making efforts to transform the waste materials into nutritious food ingredients/ food products and cosmetics/perfumes for human consumption.
- New York based Matriark Foods has been working with farmers to reduce greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, by converting imperfect and excess vegetables into pasta sauce, vegetable broth, soups and stew [18].

- Rise super flour, another product, made from whole barley following the brewing process, contains less carbohydrate and more protein. The flavor of barley is also retained after the brewing process [19].

- In 2022, Miller Harris, a UK based perfumer, launched a perfume named Myrica Muse using upcycled rose petal and patchouli oil extracted from the by-products of fresh plants [20]
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Although extensive research is being conducted on upcycling of food waste and upcycled products are available in the market, the acceptance of upcycled food by consumers is low. Studies reveal that knowledge of upcycled foods is 10% and 15% in Britain and New Zealand respectively whereas it is 35% in Turkey and 61% in Italy [21]. Consumers should be made aware of the benefits of upcycled food through social media campaigns. Promotional offers of upcycled products in stores, proper labelling and claims on the pack as well as product certification can enhance consumer awareness and acceptance. Higher consumer acceptance will favor the transition to a zero-waste sustainable economy.
References
- https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/15/13/10571
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S092422442300403X
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0960852422005594
- https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-11345-2_8
- https://biotechnologyforbiofuels.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13068-022-02222-x
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2021.792203/full
- https://ifst.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/ijfs.16297
- https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/28/11/4421
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0958694623001644
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12393-022-09330-2
- US2022232846A
- https://www.foodtechbiz.com/business-updates/arla-foods-ingredients-partners-with-enorm-to-harness-upcycling-power-of-insects
- https://www.planetarians.com/about
- https://www.kaffebueno.com/
- https://www.solabia.com/cosmetics/en/news/upcycling-beauty-when-waste-becomes-active/
- https://www.symrise.com/newsroom/article/eco-conscious-excellence-symrise-earns-top-honors-at-bsb-environment-awards-for-sustainable-beauty/
- https://winetitles.com.au/turning-wine-industry-waste-into-nutraceutical-ingredients/
- https://www.matriarkfoods.com/products
- https://www.riseproducts.co/shop/barley-flour
- https://www.millerharris.com/products/myrica-muse?variant=43146014064827
- https://www.foodnavigator.com/Article/2024/01/12/upcycled-food-consumer-perceptions

